Snoring is a common condition. In fact, it is estimated that over 45 percent of adults snore occasionally and over 25 percent snore regularly. Snoring can significantly impact your sleep, as well as the sleep of your loved ones. Snoring can be attributed to multiple factors and conditions.
What Causes Snoring?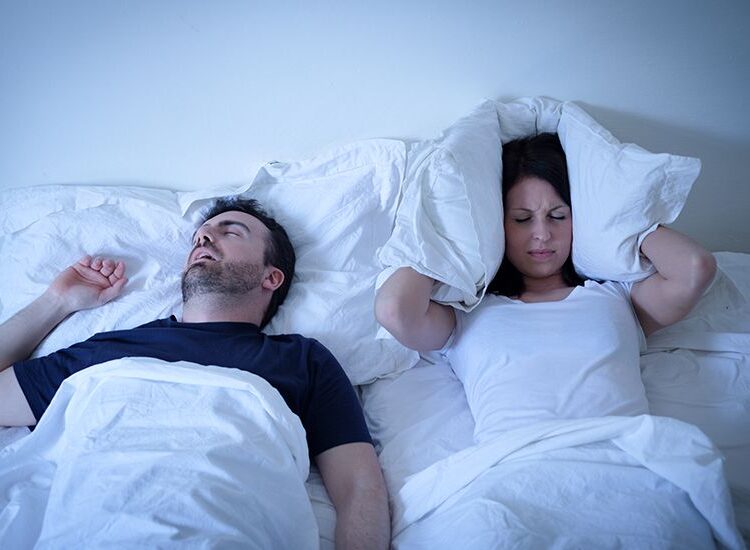
Snoring is caused by the movement and vibration of tissues near the airway in the back of the throat. During sleep, the muscles near the back of the throat relax and expand, which creates a narrowing of the airway. When we inhale and exhale, the movement of air causes these tissues to vibrate and make the sound we all know as snoring. People of any age can snore, including children. Some people are naturally more prone to snoring based upon the shape, size, and placement of the muscle and tissues in their airway. Snoring can restrict the airflow into your lungs. Many times, this causes poor sleep and irritability during the day for the person snoring as well as for others in their household. Some people who snore also suffer from sleep apnea which is a serious medical condition. Some additional risk factors for snoring include:
- Obesity
- Chronic nasal congestion
- Alcohol consumption
- Use of sedative medications
- Pregnancy
- Large tonsils, tongue, or soft palate
- Deviated septum
What’s the Difference Between Snoring and Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a condition that many people confuse with snoring. Snoring is one of the most common symptoms of OSA, but not all people who snore have sleep apnea. OSA-related snoring can be loud and sound as if a person is choking or snorting. OSA is a breathing disorder in which the airway gets blocked or collapsed during sleep, causing repeated lapses in breathing. This process disrupts the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. People with OSA will often go through repeated cycles of snoring loudly, stopping breathing, then gasping for air. Your body immediately wakes up so you can start breathing again. As you might imagine, this process is exhausting and often leads to tiredness and irritability during the daytime.
Is Sleep Apnea Dangerous?
Sleep apnea is definitely a cause for concern because it severely limits the amount of oxygen flow that is received while you are asleep. Untreated sleep apnea can be detrimental to your health. In fact, some scientific studies indicate that untreated sleep apnea can shorten your lifespan by several years!
Many health conditions are associated with sleep apnea and heavy snoring including:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Weight gain
- Anxiety
- High blood pressure
- Difficulty controlling diabetes
- Irritability
- Daytime fatigue
- ADHD
- Acid reflux
- Headaches and migraines
- Depression
- Loss of focus and memory
- Grinding teeth at night or bruxism
When Should You Talk To Your Dentist Or Doctor About Snoring?
Many instances of mild snoring are benign, but it’s important to talk with a doctor or dentist if there are signs of troublesome snoring or potential sleep apnea:
- Snoring that occurs three or more times per week
- Very loud snoring
- Snoring with gasping, choking, or snorting sounds
- Snoring accompanied by daytime drowsiness
- Snoring accompanied by lack of focus or mental sharpness
- Snoring accompanied by morning headaches
- Snoring accompanied by high blood pressure
- Nighttime teeth grinding
What Can Be Done? Snoring And Sleep Apnea Treatment Is Available At Moreland Neighborhood Dental.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, call our office at (503) 235-7000.